Exploring the anti-inflammatory potential of extracellular vesicles from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
Mairead Hyland, Claire Mennan, Daniel Tonge†, Emma Wilson#, Aled Clayton*#, Oksana Kehoe
†Keele University, #University of Chester; *#Cardiff University
Funded by the RJAH Orthopaedic Hospital Charity, Keele ACORN and Orthopaedic Institute.
This project explores a potential therapeutic treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis. It looks at the small particles, known as extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are released from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Recent studies demonstrated that both these cells and their extracellular vesicles have anti-inflammatory properties. Our group is exploring four different ways to grow these stem cells to produce a population of EVs with the most therapeutic potential.
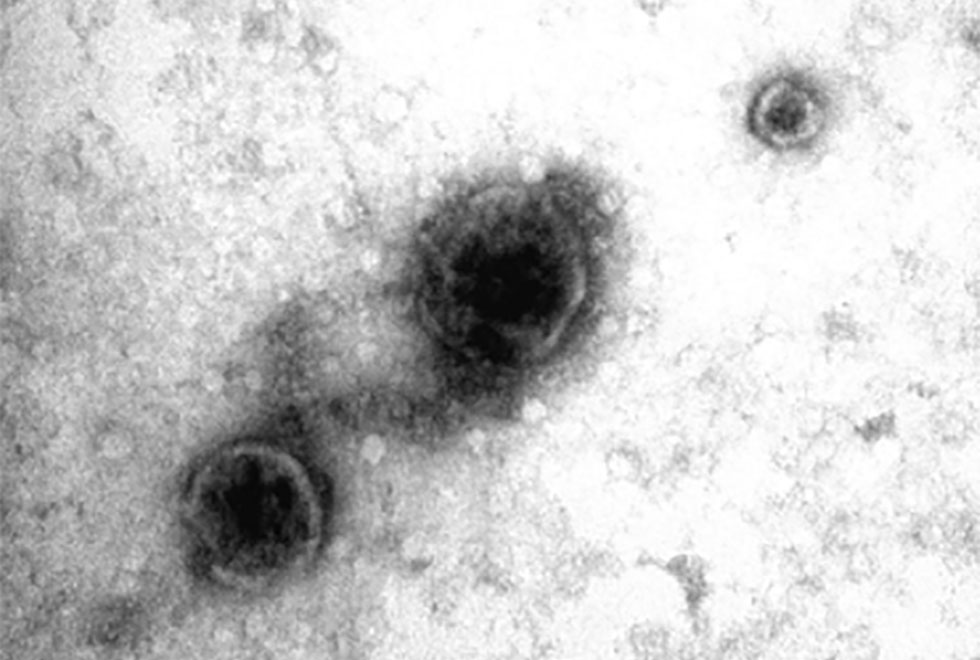
This year, we have made progress in isolating these EVs and fully characterising their properties. An images of the EVs is shown in Figure 3. We have identified a cohort of pro- and anti-inflammatory proteins contained within the EVs. Furthermore, we have successfully sequenced the genetic material – RNA- in the EVs. This research helped us to understand that growing the cells in different conditions is changing the EVs that they release.
Further research is ongoing into the functional performance of these EVs. The next step is to culture the EVs with immune cells from blood to see if these EVs can suppress the over-active immune cells. This will help us to identify which population of EVs may have the most anti-inflammatory potential for the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Figure 5. Transmission electron microscopy imaging of isolated EVs.